How high can hot air balloon go? Have you ever wondered how high a hot air balloon can soar into the sky? The answer might surprise you.
Hot air balloons, with their majestic presence and colorful designs, have captured the imagination of people for centuries.
They are not only a means of transportation but also a symbol of adventure and freedom. Pleasure flights.
Inspired by the Montgolfier brothers’ invention, offer a unique experience to witness the buoyant force in action as the flame propels the balloon upwards.
Hot air ballooning dates back to the late 18th century when the Montgolfier brothers first took flight in France.
Since then, these magnificent commercial balloons have evolved and become more sophisticated, yet they still retain their core principles.
At its most basic level, a hot air balloon consists of three essential components: the envelope (the fabric part that holds the heated air), the basket (where passengers stand), and the burner unit (which generates heat).
The parachute vent allows for controlled descent by releasing hot air, while the buoyant force counteracts gravity to keep the balloon afloat.
So how do these fascinating commercial balloons work? Well, it all comes down to one simple concept: hot air rises.
By heating up the air inside the envelope using burners fueled by propane gas, hot air becomes lighter than cool air, causing the balloon equipped with a parachute vent to ascend effortlessly into the sky.
There are various types of hot air balloons available today, each with its unique design and purpose. From traditional round Montgolfier balloons to special shapes like animals or objects, there is no limit to creativity.
These balloons are equipped with parachute vents to control the airflow and maintain stability during flight.
The flame inside the balloon’s tanks is responsible for heating the air and creating the necessary lift for the balloon to ascend. What makes hot air balloons truly remarkable is their versatility.
They can be used for recreational purposes such as sightseeing or participating in festivals, but they also serve practical functions like scientific research or advertising campaigns.
Their ability to reach different altitudes offers unparalleled views and experiences that cannot be replicated by any other mode of transportation.
Additionally, the montgolfier design, parachute vent, flame, and propane fuel are key components that contribute to the functionality and safety of hot air balloons.
In this blog post series on hot air balloons, we will delve deeper into their altitude capabilities and explore just how high these floating marvels with parachute vent can go.
So buckle up (or rather hold on tight) as we embark on an exhilarating journey through the skies, uncovering the mysteries and wonders of hot air ballooning at the top.
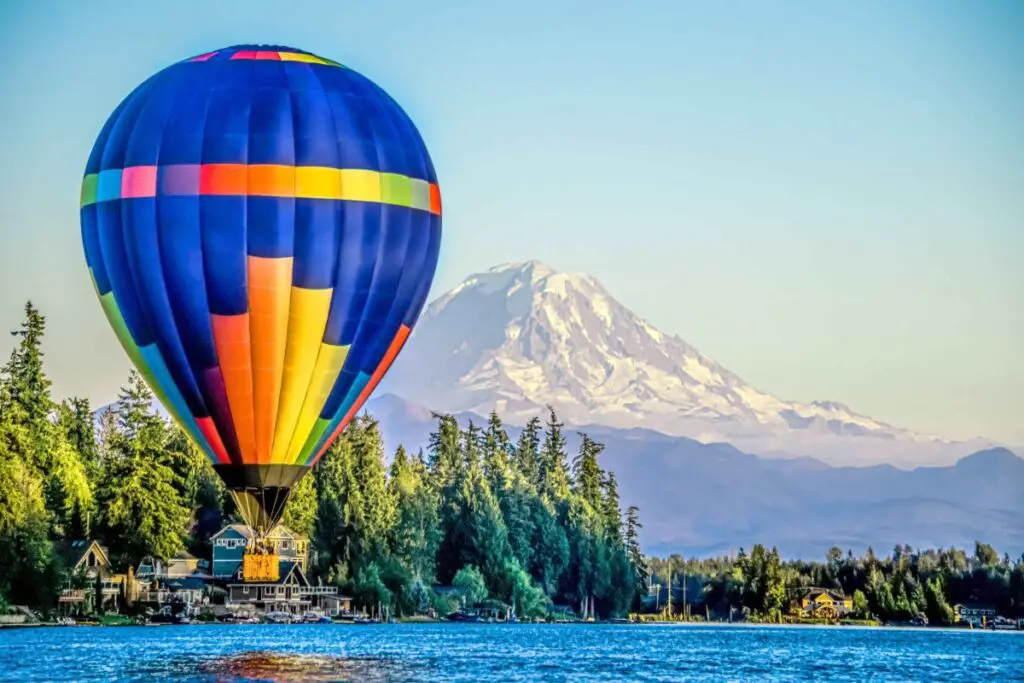

The Maximum Height of Hot Air Balloons: Reaching New Heights in the Sky
Hot air balloons have fascinated people for centuries, and one of the most common questions asked is, “How high can a hot air balloon go?”
Well, there are several factors that determine the maximum height a hot air balloon can reach, including the top of the balloon, the flame, the fabric, and the propane.
Firstly, the temperature plays a crucial role in commercial balloons. As we know, hot air rises.
So, when the flame from the propane burner inside the balloon heats up the air inside the envelope (the fabric part of the balloon), it becomes lighter than the cooler air outside.
This difference in density creates buoyancy, allowing the balloon to ascend to the top. However, as you climb higher into the atmosphere, temperatures drop significantly.
This decrease in temperature affects how high a hot air balloon can go since it reduces its lifting capacity.
Another factor to consider is the weight of the hot air balloon. Hot air balloons rely on their ability to displace enough cool air to carry their own weight and that of their passengers and equipment.
Therefore, if a balloon is overloaded or carrying excessive weight, it will not be able to ascend as high as it could with a lighter load.
Additionally, the flame from the burner, fueled by propane, is located at the top of the balloon.
Wind conditions, including wind speed and direction, play an important role in determining the safe ascent limits of a hot air balloon.
Strong winds at higher altitudes can make it challenging for pilots to control and navigate their balloons effectively, posing a risk to the flame, fabric, and overall safety of the balloon.
Therefore, pilots need to take wind speed and direction into account when planning their ascent to ensure they can safely reach the top.
The highest recorded altitude achieved by a hot air balloon
On November 26th, 2005, an impressive feat was accomplished by French adventurer Michel Fournier.
He reached an astounding altitude of 41 kilometers (25 miles) aboard his helium-filled pressurized gondola named “Le Grand Saut.”
Although this record-breaking flight used helium instead of traditional hot air for lift-off, it demonstrates just how high humans can ascend in a balloon-like vehicle with a flame, fabric, burner, and a top.
It’s important to note that this record altitude was achieved using a different type of balloon fabric and gas burner, which provides greater lifting capabilities than hot air alone.
Nevertheless, it showcases the incredible heights that can be reached with the right technology, flame, and conditions.
Challenges faced at higher altitudes for both pilots and passengers
Ascending to extreme heights in a hot air balloon presents unique challenges for both pilots and passengers. As the flame ignites the burner, the hot air fills the fabric balloon, causing it to rise.
As the balloon climbs higher into the atmosphere, oxygen levels decrease, making it harder to breathe without supplemental oxygen.
This is why most hot air balloon flights are conducted at lower altitudes where oxygen levels are sufficient. The vent in the balloon allows for controlled release of hot air, ensuring a safe descent.
Furthermore, as you reach higher altitudes during a hot air balloon ride, temperatures drop significantly. The cold becomes more intense, posing risks such as frostbite or hypothermia if proper precautions aren’t taken.
Pilots must ensure that passengers on a helium balloon are adequately dressed for these colder conditions and provide them with blankets or other means of staying warm during the flight.
The flame that heats the balloon envelope is crucial in maintaining the desired altitude and should be carefully monitored throughout the journey.
Another challenge faced at higher altitudes is the increased exposure to strong winds.
These winds can become stronger and more unpredictable as you ascend, making it more difficult to control the direction and speed of the balloon.
Pilots need to have excellent navigational skills and be prepared for sudden changes in wind patterns.
Additionally, the flame from the burner heats up the air inside the fabric balloon, causing it to rise. The vent on the top of the balloon allows the pilot to control the ascent and descent by releasing hot air.
Safety precautions taken when ascending to extreme heights
To ensure safety when ascending to extreme heights in a hot air balloon, several precautions are taken by experienced pilots.
Firstly, they carefully monitor weather conditions before takeoff to assess wind speeds at different altitudes.
If winds are too strong or gusty, they may decide against attempting a high-altitude flight. Additionally, they inspect the vent, burner, and fabric of the balloon to ensure their proper functioning.
They also consider the altitude in terms of feet to determine the feasibility of the ascent.
Pilots carry portable oxygen systems for themselves and their passengers when planning hot air balloon rides above certain altitudes where oxygen levels become insufficient.
This ensures everyone on board the balloon envelope has access to an adequate supply of oxygen throughout the journey, without compromising the vent or fabric.
Moreover, safety harnesses or seat belts made of strong fabric are essential equipment on hot air balloons at all times.
These restraints help keep passengers secure during the ascent and descent, especially at higher altitudes where turbulence or sudden movements may occur.
The balloons are equipped with a vent to control the airflow, ensuring a smooth and controlled flight.
Passengers can enjoy the breathtaking views from thousands of feet above the ground while feeling safe and comfortable.

The Speed of Hot Air Balloons: How Fast Can They Go?
Hot air balloons, made of fabric, may not be known for their speed, but they offer a unique and leisurely way to experience the skies.
On average, recreational hot air balloons typically travel at speeds ranging from 5 to 10 miles per hour.
This gentle pace allows passengers to fully enjoy the breathtaking views and serene atmosphere as they glide through the air.
The vent, located on top of the balloon, helps regulate the hot air inside. The balloons can reach heights of thousands of feet, providing an even more spectacular view.
Factors influencing the speed of a hot air balloon
Several factors come into play when determining the speed of a hot air balloon. One crucial element is wind speed.
Since hot air balloons rely on wind currents for movement, their speed is greatly influenced by the direction and intensity of the wind.
A stronger headwind can slow down a balloon’s progress, while a tailwind can help propel it forward. The fabric and vent of the balloon also affect its speed.
Another factor that affects a hot air balloon’s speed is its altitude.
As balloons ascend to higher altitudes, they encounter different wind patterns that can either assist or hinder their progress.
Pilots carefully analyze these winds, as well as the fabric and vent of the balloon, to navigate their craft and optimize their speed at various feet.
Comparison between the speed of a hot air balloon and other aircrafts
When comparing the speed of a hot air balloon, made of fabric, to other aircraft, it becomes evident that balloons, soaring thousands of feet above the ground, are more focused on tranquility than velocity.
While airplanes and helicopters can reach impressive speeds exceeding hundreds of miles per hour, hot air balloons prioritize a peaceful journey rather than rapid transportation.
Despite their slower pace, hot air balloons, made of fabric, provide an unparalleled experience by allowing passengers to savor every moment in flight.
Unlike faster aircraft, which whisk you away in a blur, ballooning offers ample time to appreciate panoramic vistas and relish in the sense of freedom suspended above the ground, thousands of feet high.
Techniques used by pilots to control and adjust the speed during flight
Although hot air balloons, made of fabric, cannot accelerate or decelerate like motorized vehicles or airplanes, skilled pilots have several techniques at their disposal to control and adjust the speed during flight.
One method involves ascending or descending to different altitudes where wind currents vary, allowing them to find a more favorable speed. The altitude is measured in feet.
Pilots can also manipulate the temperature of the air inside the balloon’s envelope.
By heating the air with the burner, they can increase buoyancy and ascend faster. Conversely, by allowing the air to cool gradually, they can slow down their descent.
Limitations on achieving high speeds due to design constraints
While hot air balloons offer a serene and graceful mode of transportation, there are inherent limitations that prevent them from achieving high speeds.
The design of a hot air balloon is primarily focused on providing lift rather than aerodynamic efficiency. The large envelope shape creates drag, which hampers acceleration and limits top speeds.
Hot air balloons lack propulsion systems like engines found in airplanes or helicopters. They rely solely on wind currents for movement, making it impossible for them to reach high velocities consistently.
Understanding Balloon Sizes and Configurations
Hot air balloons come in a variety of sizes and shapes, each designed for specific purposes. The most common shape is the traditional “teardrop” shape, which resembles an inverted lightbulb.
However, there are also other shapes such as square or rectangular balloons, which offer unique advantages in terms of stability and visibility.
Hot air balloons can range from small ones that can carry just a couple of people to massive balloons capable of carrying dozens.
Smaller balloons are often used for recreational flights or intimate gatherings, while larger ones are more suitable for commercial operations or events with a larger number of passengers.
Advantages and disadvantages associated with each size and shape
The size and shape of a hot air balloon have their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Smaller balloons are easier to handle on the ground.
Making them ideal for solo pilots or small teams. They also require less fuel to heat the air inside the envelope, resulting in lower operating costs.
On the other hand, larger balloons offer increased lift capacity, allowing them to carry more passengers or cargo.
This makes them perfect for commercial operations or special events where large groups need to be accommodated.
However, bigger isn’t always better as these balloons require more space for inflation and landing.
In terms of shape, traditional teardrop-shaped balloons provide excellent stability during flight due to their streamlined design.
This makes them less prone to turbulence and more maneuverable in the sky.
Square or rectangular-shaped balloons may not be as stable but they offer better visibility from all sides, making them popular choices for advertising purposes.
How size affects lift capacity, stability, and maneuverability
Size plays a crucial role in determining a hot air balloon’s lift capacity, stability, and maneuverability.
As mentioned earlier, larger balloons have greater lift capacity due to their increased volume of hot air. This allows them to carry more weight, whether it be passengers or cargo.
Stability is also influenced by size. Larger balloons tend to be more stable in flight as they have a larger surface area and greater mass.
This helps them resist the effects of wind gusts and turbulence, providing a smoother ride for passengers.
Smaller balloons, although less stable, can still offer an enjoyable experience under calm weather conditions.
Maneuverability is another factor affected by size. Smaller balloons are generally more maneuverable due to their lighter weight and smaller envelope size.
Pilots can easily control the ascent, descent, and direction of these balloons with precision.
Larger balloons require more effort to maneuver but can still navigate the sky effectively with skilled piloting techniques.
Popular configurations used in competitions or special events
In competitive hot air ballooning or special events, specific balloon configurations are often favored for their unique characteristics.
One popular configuration is the “special shape” balloon, which takes on various forms such as animals, objects, or characters.
These eye-catching balloons attract attention and add excitement to festivals or promotional activities.
Another common configuration is the “cluster” or “tethered” balloon setup.
In this arrangement, multiple small balloons are tethered together to form a cluster that remains stationary at a fixed altitude above the ground.
This allows spectators to enjoy the sight of several colorful balloons without them drifting away.
Considerations when choosing an appropriate size or configuration
When selecting a hot air balloon size or configuration, there are several factors to consider.
Firstly, you need to determine your intended use for the balloon – whether it’s for personal recreation, commercial operations, advertising purposes, or participating in competitions.
Next, take into account your budget and available resources. Larger balloons come with higher costs not only in terms of initial investment but also maintenance and operation expenses.
Consider the infrastructure required for inflation and landing, especially if you plan to fly from specific locations.
Lastly, consult with experienced pilots or balloon experts who can provide valuable insights based on their expertise.
They can guide you in choosing the most suitable size and configuration for your needs, ensuring a safe and enjoyable ballooning experience.

Navigating the Skies: Airspace Challenges for Hot Air Balloons
Hot air balloons may seem like a whimsical way to travel through the skies, but there are strict regulations in place to ensure the safety of both passengers and other aircraft.
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) sets guidelines for airspace usage, including specific rules for hot air balloons.
These regulations help prevent accidents and maintain order in the sky.
Hot air balloon pilots must obtain a pilot’s license and adhere to certain requirements before taking flight.
They need to be familiar with the airspace classifications, such as Class A, B, C, D, E, or G airspace. Each class has its own set of restrictions and rules that pilots must follow.
For example, flying near airports requires special attention due to high volumes of air traffic.
Hot air balloons are generally not allowed within a certain distance from airports unless they have received permission from air traffic control.
This ensures that commercial flights can take off and land without any interference.
Similarly, military zones and restricted areas pose additional challenges for hot air balloon pilots. These areas are off-limits due to national security concerns or ongoing military operations.
Pilots must be aware of these zones and avoid them at all costs.
Restrictions on flying near airports, military zones, or restricted areas
Staying clear of certain locations is crucial for safety reasons. Flying near airports can put both passengers and other aircraft at risk.
The FAA has established specific guidelines regarding distances that must be maintained between hot air balloons and airport boundaries.
Military zones are strictly controlled by armed forces around the world. These areas might contain sensitive installations or ongoing military exercises that require undisturbed operation.
As such, hot air balloon pilots need to steer clear of these zones entirely.
Restricted areas encompass various locations where access is limited or prohibited. These can include national parks, wildlife reserves, or private properties.
It is essential for hot air balloon pilots to respect these boundaries and avoid trespassing.
By adhering to these restrictions, hot air balloon pilots ensure the safety of their passengers and maintain a harmonious relationship with other airspace users.
Communication protocols with ground control or other aircraft
Communication plays a vital role in ensuring safe navigation through the skies for hot air balloons.
While hot air balloons do not have built-in communication systems like airplanes, pilots rely on alternative methods to stay connected.
Before taking flight, hot air balloon pilots coordinate with ground control personnel.
They share their intended flight path and receive crucial information about weather conditions, airspace restrictions, and any ongoing activities that may affect their journey.
In addition to ground control communication, hot air balloon pilots also need to be aware of other aircraft sharing the same airspace.
Although they might not have direct radio contact with these aircraft, visual awareness is key. Pilots must constantly scan the horizon and maintain a lookout for nearby planes or helicopters.
Hot air balloon pilots also communicate with each other during group flights or events. This ensures proper coordination and helps avoid potential conflicts while in the sky.
Strategies employed by pilots to avoid potential airspace conflicts
As hot air balloons float gracefully through the sky, it’s important for pilots to employ strategies that minimize the risk of airspace conflicts.
By following specific techniques and maintaining situational awareness, they can navigate safely alongside other aircraft.
One common strategy is altitude management. Hot air balloons can ascend or descend by adjusting the temperature of the air inside the envelope.
Pilots use this ability to change altitudes if necessary, allowing them to avoid crowded areas or conflicting flight paths.
Pilots also pay close attention to wind direction and speed when planning their flight route.
By understanding how winds move at different altitudes, they can choose paths that minimize interaction with other aircraft or potential hazards such as power lines or tall structures.
Furthermore, hot air balloon pilots often rely on visual cues to assess the flight paths of other aircraft.
They look for blinking lights, contrails, or any signs of movement in the sky to anticipate potential conflicts and adjust their own course accordingly.
Importance of weather conditions in determining safe flight paths
Weather conditions, including air temperature, wind speed and direction, cloud cover, and tennis ball, play a crucial role in determining safe flight paths. Pilots must carefully evaluate these factors before taking off.
Air temperature affects the buoyancy of the hot air balloon. Warmer temperatures provide greater lift, while colder temperatures can reduce lift or even cause descent.
Pilots need to consider these variations when planning their ascent and descent during a flight. Wind speed and direction are also critical factors for hot air balloon rides.
Pilots analyze wind patterns at different altitudes to determine suitable flight paths that minimize risks and ensure a safe journey for passengers on hot air balloon rides.

Endurance and Distance: Unveiling the Longest Balloon Flights
Hot air balloons have taken to the skies for centuries, captivating our imaginations with their graceful ascent and peaceful journeys.
Throughout history, there have been remarkable instances of endurance where these majestic balloons have stayed aloft for astonishing lengths of time.
One such record-breaking flight occurred in 1978 when the Double Eagle II successfully crossed the Atlantic Ocean, covering a distance of approximately 3,000 miles in just over 137 hours.
This monumental achievement marked a significant milestone in aviation history and showcased the incredible capabilities of hot air balloons.
Factors contributing to the endurance of a hot air balloon
The endurance of a hot air balloon is influenced by several key factors that enable it to stay airborne for extended periods. Firstly, favorable weather conditions play a crucial role.
Calm winds and stable atmospheric conditions allow pilots to maintain control and conserve fuel more efficiently.
The size and design of the balloon impact its endurance capabilities. Larger balloons with higher lifting capacities can carry more fuel, enabling longer flights without needing frequent refueling stops.
Challenges faced during long-distance flights
Embarking on long-distance flights presents unique challenges for hot air balloon pilots. One significant obstacle is managing fuel consumption effectively.
Since hot air balloons rely on burners to heat the air inside the envelope, careful monitoring of fuel usage is essential to ensure sufficient reserves for an extended journey.
Furthermore, unpredictable weather patterns can pose difficulties during long flights as pilots must navigate changing wind directions and avoid turbulent conditions that may compromise safety.
Strategies used by pilots to conserve fuel and extend flight duration
To maximize their flight duration and conserve precious fuel resources during a hot air balloon ride, experienced pilots employ various strategies.
One common technique involves flying at different altitudes to take advantage of varying wind speeds and directions.
By ascending or descending into wind layers moving in desired directions, pilots can control their course and extend their hot air balloon ride time.
Practicing efficient burner usage and maintaining optimal envelope temperature helps minimize fuel consumption during a hot air balloon ride, allowing for longer journeys.
Technological advancements that have improved endurance capabilities
Over the years, technological advancements have greatly enhanced the endurance capabilities of hot air balloons.
The introduction of lightweight and durable materials, such as ripstop nylon and high-strength synthetic fabrics.
Has significantly reduced the weight of balloon envelopes without compromising their structural integrity.
Moreover, advancements in burner technology have led to more efficient fuel combustion, enabling pilots to achieve greater endurance by utilizing fuel resources more effectively.
Steering in the Sky: Techniques for Controlling Balloon Direction
Hot air balloons may not have a steering wheel or rudder like traditional aircraft, but that doesn’t mean they can’t be controlled.
In fact, hot air balloon pilots have developed ingenious techniques to navigate through the sky.
Instead of relying on mechanical controls, they use the power of wind and altitude to guide their balloons.
Utilizing Wind Patterns and Different Altitudes to Change Direction
One of the key ways hot air balloons are steered is by taking advantage of wind patterns at different altitudes.
The wind doesn’t blow at the same speed or direction across all heights, so skilled pilots can use this variability to their advantage.
By ascending or descending to different levels in the atmosphere, they can find winds blowing in their desired direction.
For example, if a pilot wants to change course towards the west, they might ascend to a higher altitude where winds are blowing from that direction.
Conversely, if they need to head eastward, descending to a lower level with easterly winds can help them achieve their desired path.
Techniques Such as “Box” or “Figure-Eight” Patterns for Controlled Navigation
Pilots also employ specific flight patterns known as “box” or “figure-eight” maneuvers to maintain control over their balloon’s direction.
These patterns involve flying in a series of coordinated turns and straight segments that allow pilots to navigate within a certain area without drifting too far off course.
The box pattern involves flying four legs along perpendicular headings, creating a rectangular shape in the sky.
This technique allows pilots to compensate for any crosswinds and return close to their original launch point.
On the other hand, figure-eight patterns involve flying two loops connected at a central point.
This technique is useful when pilots want more flexibility in changing directions while still maintaining control over their balloon.
Adjusting Altitude to Catch Favorable Winds for Desired Direction
Another crucial aspect of steering a hot air balloon is adjusting the altitude to catch favorable winds.
As mentioned earlier, wind patterns can vary at different heights, so pilots must constantly evaluate and make altitude changes to achieve their desired direction.
For example, if a pilot wants to travel in a specific direction but encounters headwinds at their current altitude, they might ascend or descend to find more favorable tailwinds.
By skillfully managing the vertical position of the balloon, pilots can harness the power of wind currents and maintain control over their course.
Importance of Pilot Experience and Skill in Maneuvering a Hot Air Balloon
It’s essential to note that successfully steering a hot air balloon requires experience, skill, and an understanding of meteorology.
Pilots must have a deep knowledge of wind patterns and weather conditions to make informed decisions about altitude adjustments and flight maneuvers.
Furthermore, piloting a hot air balloon demands precise coordination between burner operation (which controls the heat inside the envelope) and manipulating airflow by using vents or rotation.
These actions allow pilots to fine-tune their ascent or descent rates and maintain control over direction while floating through the sky.
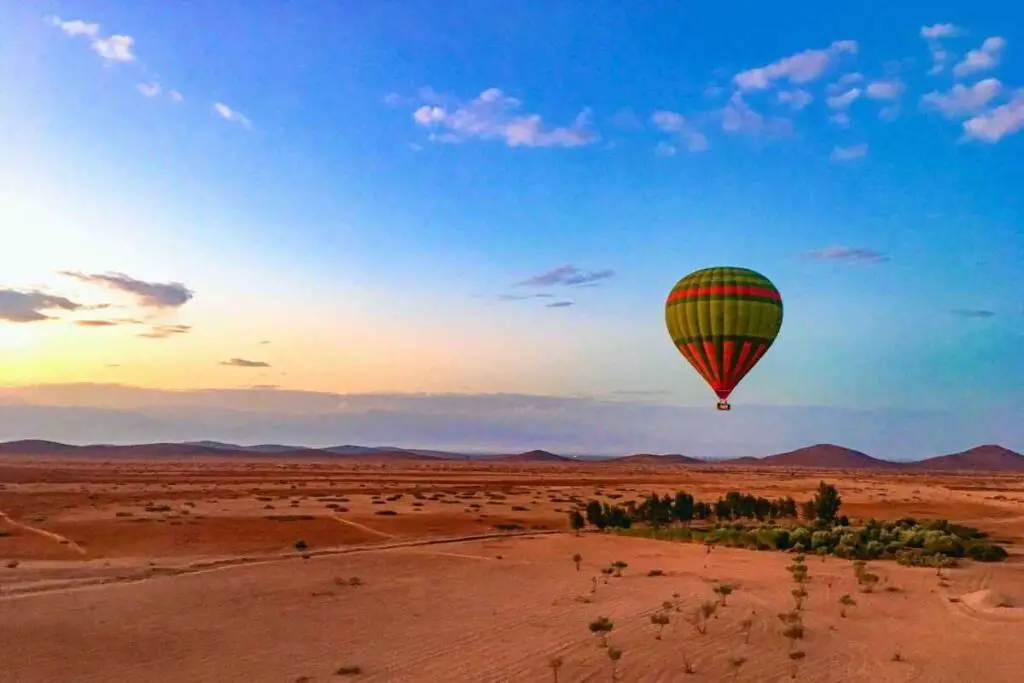

Harnessing Wind Patterns: Piloting Strategies for Balloon Maneuverability
Understanding wind currents is crucial. The direction and speed of the wind can greatly affect the balloon’s trajectory and overall maneuverability.
Experienced pilots carefully analyze wind patterns before takeoff to ensure a safe and enjoyable flight.
To understand wind currents, pilots rely on various tools such as weather forecasts, anemometers, and visual observations.
By monitoring the movement of clouds or smoke at ground level, they can estimate the direction of surface winds.
However, it’s important to note that winds at higher altitudes might differ from those near the ground.
Using wind layers at different altitudes to navigate horizontally
Hot air balloons can’t be steered in the traditional sense like airplanes or helicopters. Instead, pilots make use of different wind layers at varying altitudes to navigate horizontally.
By ascending or descending into different air masses with distinct wind directions, they can control their lateral movement.
For example, if a pilot wants to change course towards a certain destination, they may ascend or descend until they reach a favorable wind layer that will carry them in the desired direction.
This technique allows for some degree of control over horizontal movement despite not having direct steering capabilities.
Employing vertical wind speed differentials for ascent or descent control
In addition to using horizontal winds for navigation purposes, pilots also utilize vertical wind speed differentials for controlling ascent or descent.
By strategically ascending or descending into air masses with varying vertical speeds, they can effectively control their altitude.
If a pilot wishes to gain altitude quickly, they might search for an upward draft known as a thermal.
These thermals are created by warm air rising from the ground due to temperature differences and can provide significant lift when encountered by a balloon.
Conversely, if a pilot wants to descend rapidly or stabilize their altitude, they can locate a downdraft or use the parachute vent to release hot air from the envelope.
Adapting flight plans based on changing weather conditions and wind patterns
A successful balloon flight requires constant adaptation to changing weather conditions and wind patterns.
Pilots closely monitor weather forecasts leading up to their flight and make necessary adjustments to their plans accordingly.
If unfavorable weather conditions are predicted, such as strong winds or thunderstorms, pilots may choose to postpone or cancel the flight altogether.
However, if the forecast is favorable but with varying wind patterns at different altitudes, pilots must be prepared to adjust their flight path during the journey.
Maximizing maneuverability by exploiting local topography and thermal activity
To maximize maneuverability during a hot air balloon flight, pilots often take advantage of local topography and thermal activity.
By understanding how these factors interact with wind currents, they can optimize their flight path for a more enjoyable experience.
For example, flying over areas with uneven terrain or bodies of water can create localized wind patterns that differ from the surrounding areas.
These variations in wind direction can be utilized by skilled pilots to navigate around obstacles or reach specific destinations.
Similarly, thermal activity plays a significant role in balloon flights.
Pilots actively search for thermals, which are columns of rising warm air caused by differential heating of the Earth’s surface.
By finding and utilizing these thermals, pilots can extend their flight duration and potentially reach higher altitudes.
Crew Requirements: How Many People are Needed to Operate a Balloon?
Operating a hot air balloon requires a well-coordinated team effort involving the pilot, crew members, and ground support team.
Each individual plays a crucial role in ensuring the safe and successful operation of the balloon.
Pilot
The pilot is at the helm of the hot air balloon, responsible for its overall control and navigation.
They are highly trained professionals who possess extensive knowledge of aerodynamics, weather patterns, and balloon systems.
The pilot’s primary responsibility is to ensure passenger safety while providing an enjoyable experience.
They handle tasks such as determining flight paths based on wind conditions, monitoring fuel levels, adjusting altitude, and maintaining communication with air traffic control.
Crew Members
Crew members are essential for assisting the pilot before, during, and after each flight.
Their responsibilities include setting up the balloon equipment before takeoff and packing it away afterward.
During flight preparations, they help inflate the envelope by holding it open as hot air fills it. Crew members aid passengers in boarding and disembarking from the basket safely.
They also act as spotters on the ground to guide the pilot during landing by radioing information about potential obstacles or suitable landing sites.
Ground Support Team
The ground support team provides logistical assistance throughout the ballooning process. They coordinate with crew members to ensure smooth operations on-site.
This includes transporting equipment to launch sites, securing necessary permits or permissions for takeoff from private properties or restricted areas if required.
Handling paperwork related to flight clearances or insurance coverage verification when necessary.
Minimum Crew Requirements for Safe Operation of a Hot Air Balloon
To operate a hot air balloon safely, there are minimum crew requirements that must be met:
-
Pilot: A licensed pilot is mandatory for every hot air balloon flight.
-
Crew Members: The number of crew members required depends on the size and complexity of the balloon. Generally, a minimum of two crew members is necessary for most flights.
However, larger balloons may require additional crew members to handle the increased workload efficiently.
These requirements ensure that all critical tasks can be adequately managed during pre-flight preparations, flight operations, and post-flight procedures.
Having an adequate number of crew members, including a balloon pilot, allows for effective communication and smooth execution of essential duties.
Training and Qualifications Necessary for Each Crew Member’s Role
To fulfill their respective roles effectively, each crew member, including the balloon pilot, must possess specific training and qualifications.
-
Pilot: Pilots hold a valid commercial pilot certificate issued by the appropriate aviation authority in their country. They undergo extensive training programs that include theoretical knowledge assessments, practical flight experience, and examinations. Pilots must meet certain flight hour requirements to obtain or maintain their licenses.
-
Crew Members: While there are no formal certifications required for crew members, they receive comprehensive on-the-job training from experienced pilots or senior crew members. This training covers various aspects such as balloon setup and takedown procedures, safety protocols, passenger handling techniques, emergency response measures, and effective communication practices.
The combination of certified pilots with well-trained crew members ensures a high level of expertise within the team while prioritizing passenger safety.
Communication Protocols Between Pilot and Crew During Pre-Flight Preparations
Clear communication between the pilot and crew is crucial during pre-flight preparations to ensure a safe takeoff. Here are some key aspects of communication protocols:
-
Briefings: Before each flight, the pilot conducts briefings with the entire team to discuss weather conditions, flight plans, emergency procedures, and any other relevant information.
-
Radio Communication: The pilot maintains constant radio contact with ground crew members during inflation to coordinate actions effectively.
-
Hand Signals: In situations where verbal communication may be challenging, the pilot and crew members rely on standardized hand signals to convey instructions and information.
-
Emergency Protocols: The team establishes clear protocols for emergency situations, ensuring that all crew members understand their roles and responsibilities in such scenarios.
Establishing effective communication protocols minimizes the risk of misunderstandings or errors during pre-flight preparations, enhancing overall safety.
Ensuring Efficient Teamwork Throughout the Entire Ballooning Process
Efficient teamwork is vital throughout the entire ballooning process to ensure a smooth experience for passengers and safe operations.

Distance is No Barrier: Exploring the Boundless Range of Hot Air Balloons
Vast Distances Covered by Hot Air Balloons
Hot air balloons have proven their ability to cover vast distances during record-breaking flights.
These magnificent flying vessels have taken adventurers across continents and even oceans, showcasing the incredible range they can achieve.
One notable example is the 1992 flight of the Breitling Orbiter 3, which became the first hot air balloon to circumnavigate the globe.
This remarkable journey covered a distance of approximately 25,000 miles and demonstrated that hot air balloons are capable of traversing great distances.
Advantages of Using Hot Air Balloons for Long-Distance Travel
Hot air balloons offer several advantages. Unlike conventional aircraft, hot air balloons rely on wind currents for propulsion, allowing them to float effortlessly through the sky without consuming fuel.
This unique characteristic makes them an environmentally friendly option for covering substantial distances.
Hot air balloons provide passengers with a serene and captivating experience as they soar above landscapes, offering breathtaking views that no other mode of transportation can match.
Limitations on Distance Due to Fuel Capacity and Weather Conditions
Although hot air balloons can cover impressive distances, certain limitations exist that affect their range. The primary constraint is fuel capacity.
Since hot air balloons operate by heating ambient air inside their envelope, they require a constant supply of propane gas to maintain altitude and control descent.
As such, the amount of fuel carried limits how far a balloon can travel before needing to land for refueling.
Moreover, weather conditions play a crucial role in determining how far a hot air balloon can go.
Strong winds or adverse weather patterns may force pilots to alter their course or make unplanned landings for safety reasons.
While skilled pilots can navigate through varying wind currents at different altitudes to some extent, extreme weather conditions pose significant challenges and may restrict the distance a hot air balloon can cover.
Notable Achievements in Crossing Oceans or Continents with Hot Air Balloons
Despite the limitations, hot air balloons have achieved remarkable feats in crossing oceans and continents.
In 1987, Richard Branson and Per Lindstrand successfully crossed the Atlantic Ocean in their hot air balloon, Virgin Atlantic Flyer.
This historic journey covered approximately 2,900 miles from Sugarloaf Mountain in Maine, USA, to Ireland.
It demonstrated that with careful planning and favorable weather conditions, hot air balloons can conquer vast bodies of water.
Another notable achievement was the 1999 flight of the Breitling Orbiter 3 mentioned earlier. Bertrand Piccard and Brian Jones piloted this balloon as it completed its circumnavigation of the globe.
The journey took them across Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and finally back to Europe.
These extraordinary accomplishments highlight how hot air balloons can overcome geographical barriers and push the limits of human exploration.
Potential Future Developments for Extended Range Capabilities
As technology continues to advance, there is potential for future developments that could enhance the extended range capabilities of hot air balloons.
One area of exploration is utilizing alternative fuels or energy sources to power these aircraft.
By harnessing renewable energy such as solar power or hydrogen fuel cells, hot air balloons may be able to extend their range by reducing reliance on propane gas.
Advancements in weather forecasting systems could provide more accurate predictions for wind patterns at different altitudes.
This information would enable pilots to plan routes with greater precision and potentially navigate longer distances while avoiding unfavorable weather conditions.
Size Matters: Variations in Envelope and Basket Capacities
Ever wondered how high a hot air balloon can go? Well, the answer lies in the size of its envelope. The envelope is the fabric portion of the balloon that holds the heated air.
Hot air balloons come in various sizes, ranging from small to large, each with different lift capacities.
The size of the envelope determines how much hot air it can hold, which directly affects the balloon’s lifting ability.
Smaller envelopes have less volume and can carry fewer passengers or cargo, while larger envelopes have greater volume and can accommodate more weight.
Factors influencing the size of the basket or gondola
Another crucial factor affecting a hot air balloon’s capacity is the size of its basket or gondola. The basket acts as a passenger compartment or cargo area suspended beneath the envelope.
The size of the basket depends on several factors.
One significant consideration is weight distribution. Balloonists need to balance passengers, equipment, and fuel to ensure stability during flight.
If a balloon carries too much weight in one area, it may become unbalanced and pose safety risks.
Therefore, baskets are designed to accommodate specific loads while distributing weight evenly throughout.
Balancing weight distribution between passengers, equipment, and fuel
When preparing for a hot air balloon flight, pilots carefully calculate passenger weights along with any additional equipment or fuel being carried onboard.
This information helps determine how many people can safely ride in a particular balloon.
To achieve proper weight distribution within the basket, passengers may be asked to stand in designated areas based on their combined mass.
By strategically placing individuals around the basket’s perimeter or center point, pilots maintain equilibrium during flight.
Implications of larger envelopes on stability and maneuverability
While larger envelopes offer increased lift capacity and space for passengers or cargo, they also present certain implications for stability and maneuverability.
As the size of the envelope increases, so does its surface area and drag. This can affect the balloon’s ability to respond quickly to changes in wind direction or speed.
Larger envelopes may require more time and effort to inflate fully, as they contain a greater volume of air.
During flight, larger balloons tend to be less responsive to pilot inputs due to their increased mass and surface area.
Balloonists must consider these factors when choosing the appropriate envelope size for a given flight.
Customization options available for envelope and basket sizes
Hot air balloon manufacturers understand that different pilots have unique needs and preferences. Therefore, they offer customization options for both envelope and basket sizes.
There are various choices available. Pilots can select from standard shapes or opt for special shapes that add a touch of creativity to their balloons.
Special shape balloons often attract attention due to their unique designs resembling animals, objects, or characters.
Similarly, baskets come in different sizes and configurations depending on the pilot’s requirements.
Some baskets are designed for solo flights or small groups, while others accommodate larger passenger capacities or additional cargo space.
Manufacturers work closely with pilots to ensure their specific needs are metBasket dimensions, and overall system performance.

The Limitless Potential of Hot Air Balloons
Hot air balloons have come a long way since their humble beginnings as recreational vehicles.
Today, they are being used for a wide range of innovative applications that go beyond mere leisure activities.
One such application is scientific research, where hot air balloons provide a unique platform for conducting experiments and collecting data.
Imagine scientists using hot air balloons to study atmospheric conditions at various altitudes.
By ascending to different heights, researchers can gather valuable information about temperature variations, wind patterns, and even air pollution levels.
This data helps in understanding our environment better and contributes to the development of more accurate weather forecasting models.
Hot air balloon flights have become popular among tourists seeking a unique perspective on famous landmarks and scenic landscapes.
These rides offer an unparalleled experience that allows individuals to appreciate the beauty of their surroundings from high above.
From the breathtaking vistas of the Grand Canyon to the picturesque vineyards of Tuscany, hot air balloon rides provide a truly unforgettable adventure.
Scientific Research Conducted Using Hot Air Balloons
Hot air balloons have proven instrumental in advancing scientific knowledge across various disciplines.
Their ability to reach great heights while carrying heavy payloads makes them ideal for conducting experiments that require stable platforms in remote locations.
One notable example is astrophysics research conducted using high-altitude balloons equipped with telescopes and other instruments.
These specialized balloons ascend into the stratosphere, above most of Earth’s atmosphere, allowing astronomers to observe celestial bodies without interference from atmospheric distortion.
This has led to groundbreaking discoveries in our understanding of distant galaxies, cosmic background radiation, and other phenomena.
In addition to astrophysics, hot air balloons have also been utilized for atmospheric research.
Scientists studying ozone depletion or climate change often release instruments attached to small helium-filled balloons from larger hot air balloons at different altitudes.
These instruments collect valuable data as they ascend or descend, providing crucial insights into our changing environment.
Promoting Tourism Through Hot Air Balloon Rides
Hot air balloon rides have become a popular attraction for tourists worldwide.
Offering a unique and awe-inspiring experience, these flights allow visitors to see famous landmarks and natural wonders from an entirely different perspective.
Imagine floating gently above the pyramids of Egypt or soaring over the Serengeti during the annual wildebeest migration.
These unforgettable moments create lasting memories and draw travelers from all corners of the globe.
The tourism industry has recognized this potential, leading to the establishment of hot air balloon operations in many tourist destinations.
Whether it’s exploring ancient ruins, admiring stunning landscapes, or observing wildlife in their natural habitats, hot air balloon rides provide an unparalleled adventure that appeals to adventurers seeking a new way to explore the world.
Advertising and Marketing Opportunities with Branded Hot Air Balloons
Branded hot air balloons offer companies a unique advertising platform that captures attention both on the ground and in the sky.
By featuring their logos, slogans, or product designs on these floating billboards, businesses can create a memorable brand presence that stands out from traditional advertising methods.
Imagine attending a festival where colorful hot air balloons adorned with company logos dot the sky.
The visual impact is undeniable as these branded balloons capture people’s attention from miles away.
This form of aerial advertising not only generates brand awareness but also creates an emotional connection with consumers who associate the excitement and beauty of hot air ballooning with the advertised brand.
Furthermore, branded hot air balloons are often used for promotional events and marketing campaigns.
Companies can offer exclusive rides or organize competitions where winners get to experience a once-in-a-lifetime balloon flight.
These initiatives generate buzz and excitement around brands while providing customers with unique experiences they will never forget.
Inspiring Artistic Expressions Through Special-Shaped Balloons
Hot air balloons have evolved beyond their traditional spherical shape, giving rise to a whole new world of artistic expressions through special-shaped balloons.

Conclusion
Hot air balloons have captured the imagination of people for centuries, and it’s no wonder why.
These majestic vessels offer a unique perspective of the world from above, providing an unparalleled sense of freedom and adventure.
In this conclusion, we will summarize the key points discussed in the previous sections and highlight the limitless potential that hot air balloons possess.
Throughout our exploration, we’ve discovered that hot air balloons can reach impressive heights, allowing passengers to soar high above the ground and experience breathtaking views.
While there is no definitive limit to how high a hot air balloon can go, factors such as atmospheric conditions and safety considerations play a crucial role in determining their maximum altitude.
Speed is another aspect that sets hot air balloons apart. Although they may not be known for their swiftness like other aircraft, they offer a leisurely pace that allows passengers to fully immerse themselves in the journey.
It’s not about rushing from one destination to another but rather embracing the slow and serene nature of ballooning.
Understanding balloon sizes and configurations is essential for those interested in taking flight.
Different envelope sizes and basket capacities cater to varying needs, whether it be an intimate ride for two or a larger group excursion.
This versatility ensures that there is a suitable option for everyone who wishes to experience this extraordinary form of travel.
Navigating the skies presents its own set of challenges for hot air balloon pilots.
Airspace regulations must be adhered to ensure safety among other aircraft while maintaining control over direction and altitude.
Pilots employ techniques such as steering with wind patterns and harnessing wind currents strategically to maneuver their craft effectively.
The endurance and distance capabilities of hot air balloons are truly remarkable.
Throughout history, adventurers have embarked on long-distance flights lasting hours or even days, pushing boundaries and achieving incredible feats.
These epic journeys showcase just how far these magnificent vessels can take us.
Operating a hot air balloon requires a dedicated crew, with each member playing a vital role in ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience.
From the pilot to the ground crew, teamwork is essential for successful flights. The number of people needed varies depending on factors such as balloon size and complexity.
Hot air balloons offer an unparalleled range that knows no bounds.
Whether floating over vast landscapes or drifting above bustling cities, these vessels can transport you to places unreachable by traditional means of transportation.
The freedom to explore new horizons and discover hidden gems from the sky is an invitation that should not be missed.
In conclusion, hot air balloons possess limitless potential in terms of height, speed, endurance, distance, and maneuverability.
They provide a unique perspective of the world while offering a sense of adventure and freedom like no other mode of travel.
So why not seize the opportunity to embark on your own hot air balloon adventure? Take to the skies and create memories that will last a lifetime.

FAQs
1. How safe are hot air balloon flights?
Hot air balloon flights are generally considered safe when operated by experienced pilots following strict safety protocols. However, it’s important to choose reputable companies with well-maintained equipment and trained staff to ensure a safe and enjoyable experience.
2. How many people can fit in a hot air balloon basket?
The capacity of hot air balloon baskets varies depending on their size and configuration. Smaller balloons may accommodate two to four passengers, while larger ones can carry up to 20 or more individuals. It’s best to check with the specific operator for their basket capacity.
3. Can I control where a hot air balloon goes?
While you cannot directly control the direction of a hot air balloon like you would with an airplane or car, skilled pilots can navigate using wind patterns at different altitudes. By ascending or descending into layers with varying wind speeds and directions, they can guide the balloon towards desired destinations within certain limitations.
4. Are there any age restrictions for hot air balloon rides?
Age restrictions for hot air balloon rides may vary depending on the operator and local regulations. In many cases, children must be a certain age (often around six or older) and accompanied by an adult. It’s advisable to check with the specific company beforehand to ensure compliance with any age requirements.
5. What should I wear during a hot air balloon ride?
It’s recommended to dress comfortably and in layers, as temperatures can change at higher altitudes. Wearing closed-toe shoes is important for safety reasons. Avoid loose clothing that could get caught in equipment and consider bringing a hat and sunscreen for sun protection.
7. Can I bring my camera or phone on a hot air balloon ride?
Yes, you are usually allowed to bring cameras or phones onboard a hot air balloon ride to capture memories of your journey.










Leave a Reply